3D Printing: 5 Ways it’s Transforming US Manufacturing
3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing in the United States through rapid prototyping, customized production, decentralized manufacturing, innovative material use, and significant cost reduction, leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness.
The manufacturing landscape in the United States is undergoing a seismic shift, and 5 Ways 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Manufacturing in the United States are at the forefront of this transformation.
Rapid Prototyping and Accelerated Innovation
One of the most immediate impacts of 3D printing on U.S. manufacturing is the acceleration of prototyping processes. Traditional prototyping methods can be time-consuming and expensive, often involving tooling and machining that delays the innovation cycle. 3D printing offers a faster and more agile alternative.
Speeding Up the Design Process
With 3D printing, manufacturers can create physical prototypes in a matter of hours or days, rather than weeks or months. This speed allows designers and engineers to test and refine their ideas more quickly, leading to faster product development cycles.
Reducing Prototyping Costs
The cost savings associated with 3D printing are also significant. By eliminating the need for expensive tooling and reducing material waste, companies can prototype more affordably, allowing for more experimentation and innovation.
- Material Flexibility: 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, enabling prototypes to closely mimic the final product.
- Design Freedom: Complex geometries and intricate designs can be easily prototyped, pushing the boundaries of innovation.
- Iterative Improvement: Rapid iteration leads to better designs and more refined products in a shorter time frame.
- Testing and Validation: Physical prototypes allow for real-world testing and validation, ensuring product performance and reliability.
In conclusion, rapid prototyping through 3D printing is not just about speed; it’s about empowering manufacturers to innovate more effectively and efficiently, giving them a competitive edge in the global market.
Customized Production and Mass Personalization
Another transformative aspect of 3D printing is its capability to facilitate customized production and mass personalization. Traditional manufacturing processes are often geared towards mass production of standardized items, making it difficult and expensive to produce customized products.
Meeting Unique Customer Needs
3D printing enables manufacturers to create products tailored to the specific needs and preferences of individual customers. This level of customization was previously unattainable with traditional methods.
On-Demand Manufacturing
The ability to produce items on demand also reduces the need for large inventories, minimizing storage costs and the risk of obsolescence. This is particularly valuable for industries dealing with rapidly changing consumer demands.
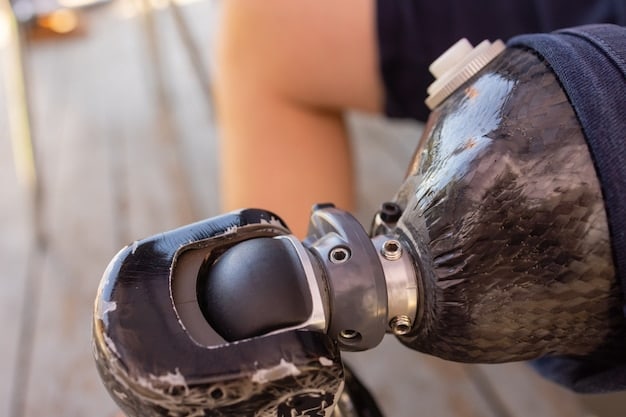

- Medical Applications: Custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides are revolutionizing healthcare, improving patient outcomes.
- Aerospace Industry: Lightweight, customized components for aircraft and spacecraft enhance performance and reduce fuel consumption.
- Consumer Goods: Personalized products, from shoes to jewelry, offer unique value and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Automotive Sector: Customized car parts and accessories allow for greater design flexibility and personalization.
Ultimately, customized production through 3D printing is reshaping the relationship between manufacturers and consumers, fostering a new era of personalization and customer-centric design.
Decentralized Manufacturing and Supply Chain Resilience
3D printing is also contributing to the decentralization of manufacturing, shifting production away from centralized factories to smaller, more localized facilities. This shift offers several benefits, including increased supply chain resilience and reduced transportation costs.
Local Production, Global Reach
By enabling local production, 3D printing reduces the reliance on long and complex supply chains, making manufacturers less vulnerable to disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical events, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Reduced Transportation Costs
Producing goods closer to the point of consumption reduces transportation costs and carbon emissions, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing ecosystem.
- Remote Locations: 3D printing enables manufacturing in remote locations, such as military outposts or research stations, where traditional manufacturing is impractical.
- Disaster Relief: Rapid deployment of 3D printers can provide essential supplies and equipment in disaster-stricken areas.
- Small Businesses: 3D printing empowers small businesses to start manufacturing operations with minimal capital investment.
- Global Expansion: Companies can expand their reach by establishing localized production facilities in new markets.
In conclusion, decentralized manufacturing through 3D printing is creating a more resilient and efficient manufacturing landscape, fostering local economies and reducing global dependencies.
Innovative Material Use and Advanced Manufacturing Processes
The versatility of 3D printing extends to the innovative use of materials, enabling manufacturers to explore new possibilities and develop advanced manufacturing processes. Traditional manufacturing methods are often limited by the types of materials they can process, whereas 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites.
New Materials, New Possibilities
This material flexibility opens up new avenues for product design and functionality, allowing manufacturers to create items with enhanced properties, such as increased strength, reduced weight, or improved thermal resistance.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
3D printing also facilitates the development of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as lattice structures and topological optimization, which were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.

- Aerospace Applications: Lightweight, high-strength components for aircraft and spacecraft improve performance and reduce fuel consumption.
- Automotive Industry: Durable, lightweight parts for cars and trucks enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Medical Implants: Biocompatible materials and customized designs improve the integration and performance of medical implants.
- Construction Industry: 3D-printed building components offer sustainable and cost-effective construction solutions.
Ultimately, innovative material use in 3D printing is not only transforming manufacturing processes but also driving innovation across various industries, leading to the development of new and improved products.
Cost Reduction and Increased Efficiency
One of the most compelling reasons for manufacturers to embrace 3D printing is its potential to significantly reduce costs and increase efficiency. Traditional manufacturing processes often involve high setup costs, long lead times, and significant material waste, all of which can impact profitability.
Lowering Production Costs
3D printing reduces or eliminates these costs, making it a more economically viable option for a wide range of manufacturing applications. The ability to produce parts on demand minimizes the need for large inventories, reducing storage costs and the risk of obsolescence.
Improving Operational Efficiency
The streamlined production process also improves operational efficiency, allowing manufacturers to respond more quickly to changing market demands and customer needs.
- Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing minimizes material waste by only using the material necessary to create the part.
- Faster Production: 3D printing significantly reduces lead times, enabling faster product development and delivery.
- Lower Labor Costs: Automated production processes reduce the need for manual labor, lowering overall production costs.
- Energy Efficiency: 3D printing can be more energy-efficient than traditional manufacturing processes, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
In conclusion, cost reduction and increased efficiency are key drivers of the 3D printing revolution, making it an increasingly attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve their bottom line and enhance their competitiveness.
The Future of 3D Printing in US Manufacturing
The ongoing advancements in 3D printing technology promise even greater transformations for U.S. manufacturing in the years to come. As 3D printers become faster, more accurate, and more versatile, they will be capable of producing an even wider range of products with greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Integration with AI and Automation
The integration of 3D printing with artificial intelligence (AI) and automation will further streamline manufacturing processes, enabling manufacturers to optimize designs, predict performance, and automate production tasks. This convergence of technologies will lead to smarter, more efficient, and more responsive manufacturing operations.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainability will drive the adoption of 3D printing as a means of reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental impact. As manufacturers seek to adopt more sustainable practices, 3D printing will play an increasingly important role in their efforts.
- Advanced Materials: Continued development of new materials will expand the range of applications for 3D printing.
- Scalability: Improvements in scalability will enable manufacturers to produce larger volumes of parts with 3D printing.
- Customization: Enhanced customization capabilities will allow for even greater personalization of products.
- Accessibility: Increased accessibility will make 3D printing more affordable and accessible to small businesses and individuals.
In the end, the future of 3D printing in U.S. manufacturing is bright, with ongoing innovations promising to transform the way products are designed, manufactured, and delivered to customers.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Rapid Prototyping | Speeds up design process and reduces costs, enabling faster innovation cycles. |
| 🪡 Customization | Allows for mass personalization, meeting unique customer needs across industries. |
| 🏘️ Decentralization | Enables local production, enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing transport costs. |
| 🌿 Material Innovation | Facilitates use of diverse materials, enhancing product properties and advanced processes. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds three-dimensional objects from a digital design. It works by layering materials such as plastic, metal, or composites, one layer at a time, until the object is complete.
▼
The primary benefits include faster prototyping, customized production, decentralized manufacturing, innovative material use, and significant cost reduction. These benefits lead to improved efficiency and competitiveness.
▼
3D printing enables decentralized manufacturing, reducing reliance on long supply chains. Local production minimizes disruptions from natural disasters or geopolitical events, enhancing supply chain resilience.
▼
Industries such as aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods are benefiting significantly. 3D printing allows for customized parts, improved performance, and innovative designs in these sectors.
▼
Future trends include integration with AI and automation, the development of advanced materials, improved scalability, and increased customization capabilities. These advancements promise even greater transformations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 5 Ways 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Manufacturing in the United States represent a fundamental shift in how products are conceived, designed, and produced. From accelerating prototyping to enabling mass personalization and fostering supply chain resilience, 3D printing is empowering manufacturers to be more innovative, efficient, and competitive in the global marketplace.





