Design Thinking in Education: Empowering US Students for Innovation
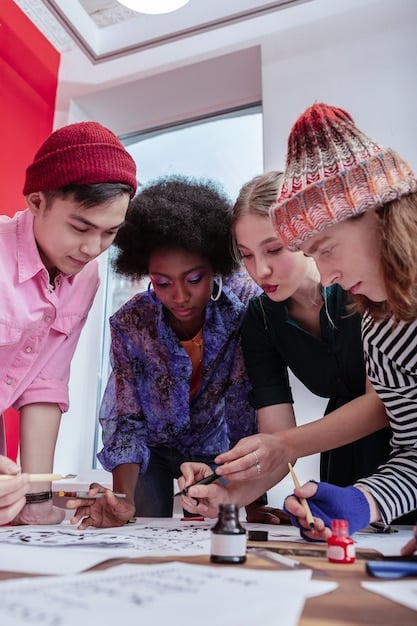

Design Thinking in Education equips US students with a problem-solving framework that fosters creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking, enabling them to tackle real-world challenges effectively.
Design Thinking in Education is revolutionizing the way US students learn by empowering them to become innovative problem-solvers. By embracing a human-centered approach, students develop crucial skills needed to address complex real-world problems and shape a brighter future.
What is Design Thinking in Education?
Design Thinking, traditionally utilized in business and design, is now making waves in education. It offers a structured yet flexible framework for fostering creativity and problem-solving skills among students.
This approach shifts the focus from rote memorization to active engagement, allowing students to take ownership of their learning and develop innovative solutions to relevant challenges.
The Core Principles of Design Thinking
Design Thinking is anchored by a set of core principles that guide the problem-solving process.
- Empathize: Understanding user needs and perspectives through research and observation.
- Define: Clearly articulating the problem to be solved based on gathered insights.
- Ideate: Brainstorming a wide range of potential solutions.
- Prototype: Creating tangible representations of ideas for testing and refinement.
- Test: Gathering feedback on prototypes and iterating towards an optimal solution.
These principles provide a roadmap for students to explore, experiment, and learn from their successes and failures, fostering resilience and adaptability.
Ultimately, design thinking in education moves the student into the shoes of a designer, analyst and executor of ideas. It is a move away from teaching children what to think and a new move into how to think.
In essence, Design Thinking in Education provides US students with a framework to not only solve problems but to innovate and create solutions that make a real impact.
The Benefits of Design Thinking for US Students
Integrating Design Thinking into the US education system offers numerous benefits for students, preparing them for success in an ever-evolving world.
These benefits extend beyond academic achievement, fostering essential life skills and a growth mindset.
Boosting Creativity and Innovation
Design Thinking encourages students to think outside the box and explore unconventional approaches to problem-solving.
By embracing experimentation and iteration, students develop their creative potential and learn to generate innovative solutions.
- Encourages risk-taking and experimentation without fear of failure.
- Fosters a culture of collaboration where diverse perspectives are valued.
- Develops the ability to connect seemingly disparate ideas and concepts.
These skill sets become invaluable as they progress through higher education and into their professional careers.
Moreover, as the world of business becomes more fast paced, it become more necessary for employees to have the skills to create quick innovative solutions to ongoing challenges and new challenges.
In short, Design Thinking is a way to prime US citizens for a future with less rote work and greater opportunities for value added work.
Implementing Design Thinking in US Classrooms
Successfully integrating Design Thinking into US classrooms requires careful planning, teacher training, and a supportive school environment.
Here are key strategies for educators looking to embrace this innovative approach.
Integrating Design Thinking into the Curriculum
Design Thinking can be seamlessly integrated into various subjects by framing lessons around real-world problems that students can investigate and solve.
Project-based learning provides an ideal platform for applying the Design Thinking process, encouraging students to explore topics in depth and develop tangible solutions.
- Start with simple challenges that allow students to grasp the basic principles.
- Provide clear guidelines and resources to support the Design Thinking process.
- Encourage collaboration and peer feedback throughout the project.
Teachers also have to ensure that the principles of design thinking are taught in a rigorous and thorough matter. Design Thinking is not just a fun exercise for students, but it must have a solid fundamental backing of information and ideas as well.
Therefore, it is also important for educators to be well versed in the skills that the students are developing in order to offer additional help and guidance as needed.
The Importance of Teacher Training
Effective implementation of Design Thinking relies heavily on well-trained teachers who can guide students through the process and cultivate a creative learning environment.
Professional development programs can equip teachers with the knowledge and skills needed to facilitate Design Thinking projects effectively.

By shifting the emphasis from traditional teaching to student-led exploration, educators can empower students to become active participants in their learning journey.
Ultimately, it is the investment placed in educators that will dictate the future level of success design thinking can play in the world of education.
Examples of Successful Design Thinking Projects
Across the US, numerous schools and educators have successfully implemented Design Thinking projects, empowering students to tackle real-world challenges and make a positive impact.
These projects showcase the versatility of Design Thinking and its ability to engage students in meaningful learning experiences.
Addressing Community Needs
Design Thinking projects often focus on addressing specific needs within the local community, allowing students to apply their skills to solve problems that directly affect their lives.
Examples include designing sustainable solutions for waste management, creating accessible playgrounds for children with disabilities, or developing campaigns to promote mental health awareness.
By working on projects that have a tangible impact, students develop a sense of purpose and a commitment to social responsibility.
Moreover, students learn to become advocates for their peers and understand the necessity to communicate change in order to see it happen. Ultimately as they grow they may seek out to be an advocate at the macro or even global level.
While design thinking is great for innovation and value creation, the best results come when the end goal of the problems and innovation is value for the social good.
Challenges and Solutions in Design Thinking Education
While its advantages are considerable, incorporating Design Thinking into US education isn’t without its own set of challenges.
But understanding the challenges allows educators to better adapt to what is in front of them.
Overcoming Resource Constraints
Limited resources, including time, funding, and materials, can pose significant obstacles to implementing Design Thinking projects effectively.
Creative solutions include seeking grants and partnerships, utilizing readily available materials, and leveraging digital tools to minimize costs.
- Seeking funding from educational grants and local community organizations.
- Using readily available and recycled materials for prototyping.
- Collaborating with community partners for resources and expertise.
Moreover, there are many free resources online that can educate students and teachers alike in the core principles of design thinking. As online resources become more and more pervasive, the ability for educators to teach this becomes easier and easier.
However, some teachers are not native to utilizing online resources, so they may need additional courses in how they can locate these resources. There are also many courses teaching teachers that are not free.
As the education space grows, there will need to be an increasing focus on resources that aid teachers in helping students with design thinking.
This will allow easier adaption into schools both rich with funding and schools that are less rich with funding.
The Future of Design Thinking in US Education
The future of Design Thinking in US education looks promising, with increasing recognition of its potential to transform learning and prepare students for the challenges of the 21st century.
As more educators embrace this innovative approach, it promises to shape the future generations of learners and innovators.
Expanding Access to Design Thinking
Efforts are underway to expand access to Design Thinking education for all students, regardless of their socioeconomic background or geographic location.
Initiatives include offering Design Thinking workshops and programs in underserved communities, creating online resources for remote learners, and integrating Design Thinking into teacher education programs.
By ensuring equitable access, we can empower all students to develop the skills and mindsets needed to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Moreover, as educators continue to understand what is needed for a quality integration of design thinking into the classroom, the opportunity will continue to expand and scale.
While there are challenges to it, that should not deter efforts in improving integration and scalability of design thinking.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💡 Innovation | Design Thinking sparks student innovation through hands-on problem-solving. |
| 🤝 Collaboration | Teamwork enhances diverse perspectives in design thinking projects. |
| 🚀 Problem Solving | Students tackle real-world issues with a structured design approach. |
| 🍎 Education | Design Thinking transforms rote teaching into student engagement . |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The main goal is to foster innovative problem-solving skills, enabling students to tackle real-world challenges effectively and creatively, while developing a human centered way of thinking.
▼
Design Thinking shifts from rote memorization to active engagement, encouraging students to own their learning and develop innovative solutions. It relies less on test taking and more on practical skills.
▼
The core principles include empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing. These steps guide students through a structured yet flexible problem-solving process. By understanding all these steps, value can be created.
▼
Teachers can integrate Design Thinking by framing lessons around real-world problems and using project-based learning to encourage in-depth exploration and tangible solution development. There are ample resources online that aid teachers.
▼
Effective implementation requires well-trained teachers equipped with the knowledge and skills to facilitate Design Thinking projects. Professional development programs are essential for this kind of success in the classroom.
Conclusion
Design Thinking in Education is more than just an instructional method; it is a transformative approach that empowers US students to become creative problem-solvers and active participants in shaping their future. By embracing this innovative framework, educators can unlock students’ full potential and prepare them for success in an ever-changing world.





